Bonding and Structure* — the science sauce
Formation of a permanent dipole - (polar covalent) bond A polar covalent bond forms when the elements in the bond have different electronegativities . (Of around 0.3 to 1.7) When a bond is a polar covalent bond it has an unequal distribution of electrons in the bond and produces a charge separation, (dipole) δ+ δ-ends. The element with the.

5 Shape of molecules
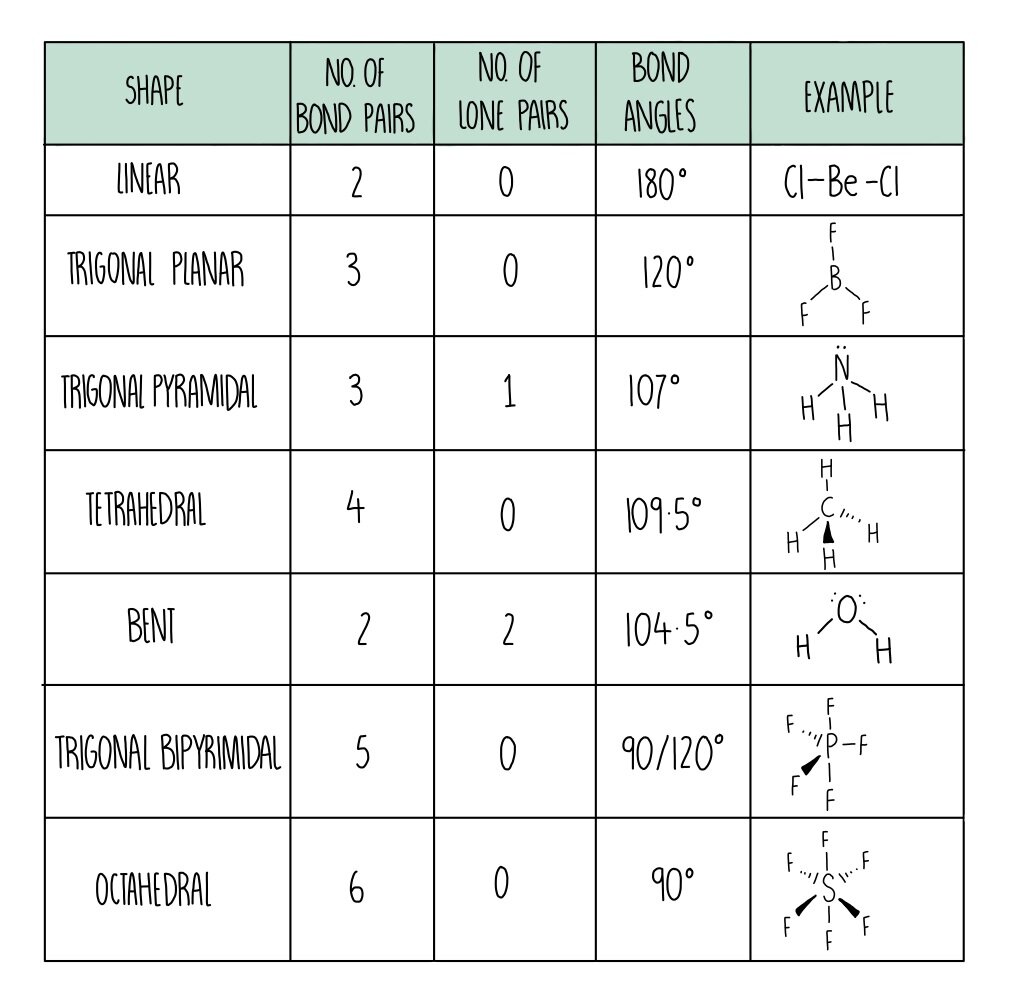
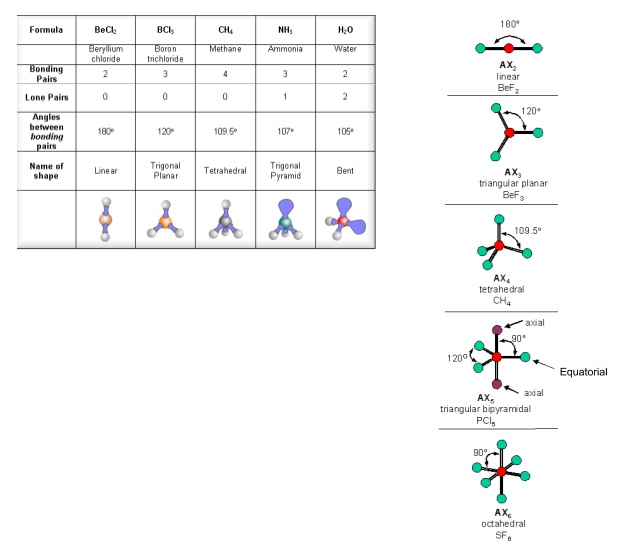
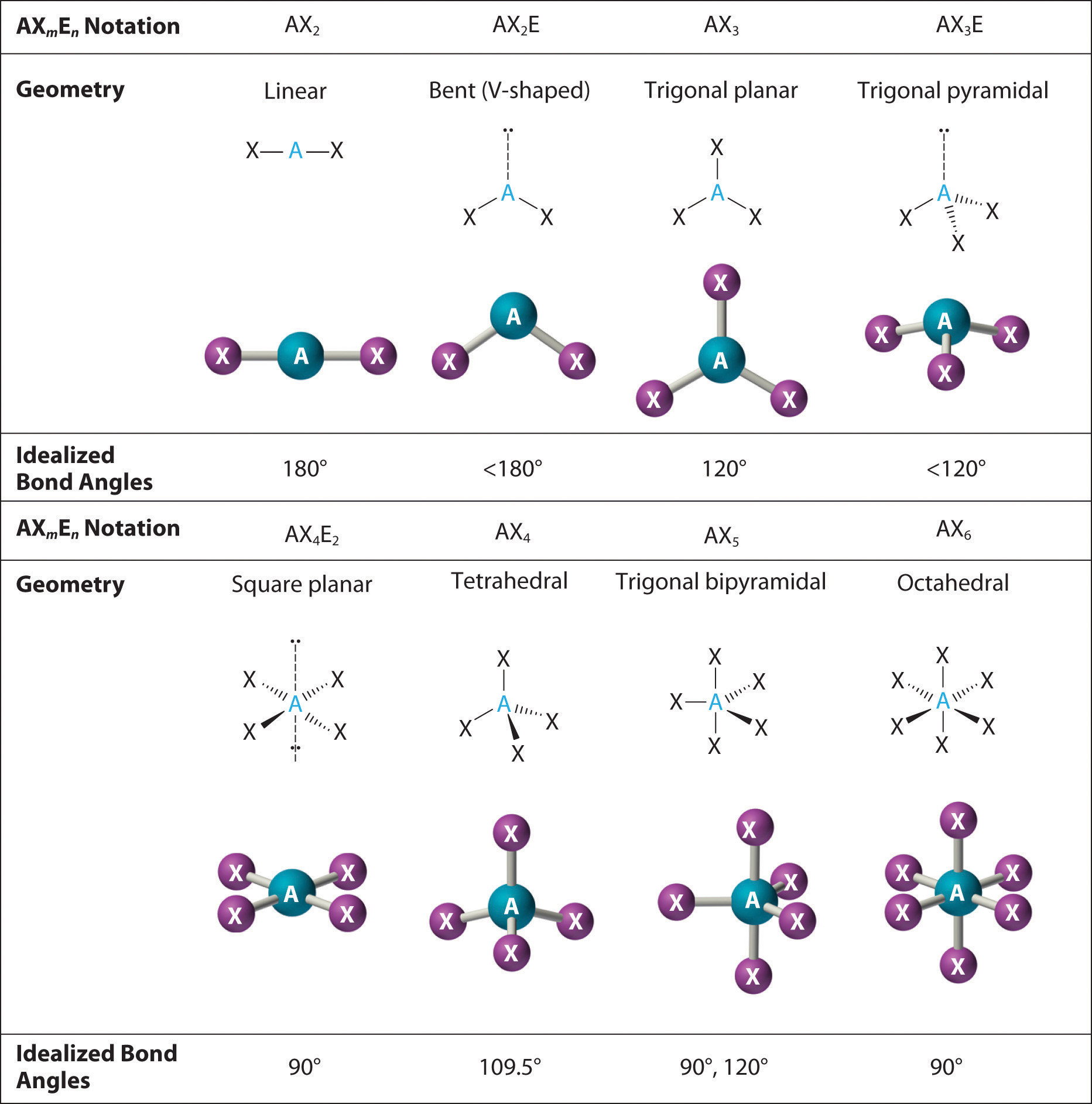
The way this works is best shown by examples. Check your A-level specification to find out which shapes you have to KNOW and which ones you need to be able to WORK OUT. Start with two electron pairs, both bonding (eg BeCl 2). The electrons spread to opposite sides of the imaginary sphere and so the molecule is LINEAR with a bond angle of 180 o.
Alevel Chemistry AQA Notes Atomic Structure ALEVEL NOTES
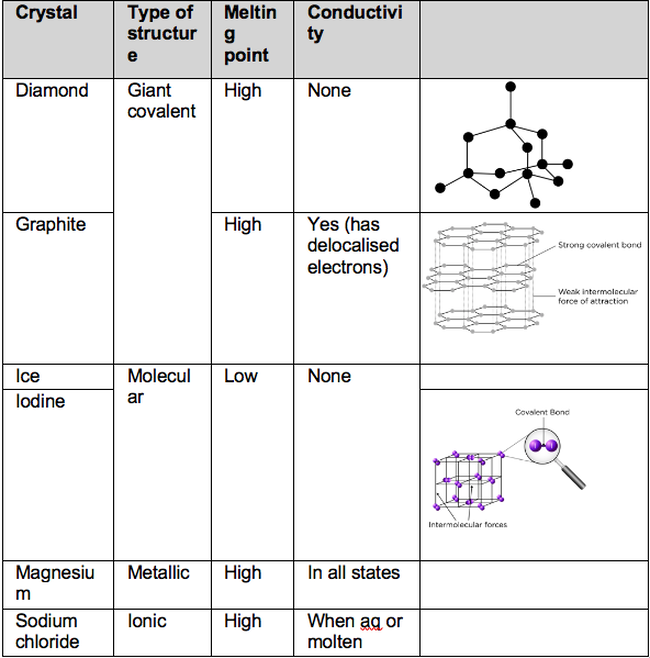
3.1.3.1 Ionic Bonding. Ionic bonding occurs between a metal and a non-metal. Electrons are transferred from the metal to the non-metal to achieve full outer shells. When the electrons are transferred, it creates charged particles called ions. Oppositely charged ions attract through electrostatic forces to form a giant ionic lattice.
Shapes of molecules a2levellevelrevision, chemistry, bondingandstructure, shapes
The valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR) predicts the shape and bond angles of molecules; Electrons are negatively charged and will repel other electrons when close to each other; In a molecule, the bonding pairs of electrons will repel other electrons around the central atom forcing the molecule to adopt a shape in which these repulsive forces are minimised

Chem Bond Angle Scientific Tutor
the H atoms down (angles reduced to 107. o); and H. 2. O has two lone pairs, which repel the H atoms even more (angle now 104.5. o): bond angle 104.5. o. water: non -linear . H H O. bond angle 107 ammonia - pyramidal . H H. ammonia . N. H N H H H + The ammonium ion has four bonding pairs of electrons in the valence shell (one of theses being.

molecular shape and angles Teaching chemistry, Chemistry education, Chemistry lessons
We explore electron pair repulsion theory and look at how this explains the shapes of molecules including molecules with multiple bonds, such as double bonds. We then look at the shapes and bond angles in linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal and octahedral molecules. In the next video, we look at the shapes of molecules.

What is the bond angle of OF2?
The videos below are from the YouTube channels MaChemGuy and Mr C Dunkley. Subscribe to keep up to date with the latest videos. Contents [ hide] 1 Overview: Bonding and Structure. 2 Ionic Bonding. 3 Properties of Ionic Compounds. 4 Covalent Bonding. 5 Coordinate/Dative Covalent Bonding.

A Level Chemistry Bond Angles And Shapes Chemical Formulas
When determining the shape and bond angles of a molecule, the following VSEPR rules should be considered: Valence shell electrons are those electrons that are found in the outer shell;. Philippa has worked as a GCSE and A level chemistry teacher and tutor for over thirteen years. She studied chemistry and sport science at Loughborough.
OCR AS Chemistry Notes Foundations in Chemistry Electrons, Bonding And Structure ALEVEL NOTES
Shapes of Molecules. The valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR) predicts the shape and bond angles of molecules. Electrons are negatively charged and will repel other electrons when close to each other. In a molecule, the bonding pair of electrons will repel other electrons around the central atom forcing the molecule to adopt a.

XeCl4 Lewis Structure, Geometry, Hybridization, and Polarity Techiescientist
The greater the repulsion force between two pairs of electrons, the more far apart the two pairs of electrons will be and hence the larger the bond angle between them. As lone pairs of electrons have the strongest repelling effect, there is the greatest bond angle between them. Bonding - Molecular Shapes (A-Level Chemistry)

chemical bonding Brilliant Math & Science Wiki
Edexcel Chemistry A-level - Shapes and Bond Angles. Q22. Boron and aluminium are in the same group of the Periodic Table. Both form compounds with chlorine and with fluorine. Boron reacts directly with chlorine to produce a covalently bonded compound, BCl 3. (i) Write the equation for this reaction. State symbols are not required.

A Level Chemistry at the Alun Why do you get that 180 bond angle between water molecules?
Because the lone pair of electrons occupies more space than the bonding pairs, we expect a decrease in the Cl-Sn-Cl bond angle due to increased LP-BP repulsions. D With two nuclei around the central atom and one lone pair of electrons, the molecular geometry of SnCl 2 is bent, like SO 2, but with a Cl-Sn-Cl bond angle of 95°. The.
Bond Angle For Bent Molecular Geometry
In this video, we look at the shapes of molecules where there is no lone pair of electrons on the central atom. We explore electron pair repulsion theory and.

23+ Molecular Geometry Chart With Bond Angles Image GM
A-Level Chemistry - Bond Angles. 9 terms. Harv234. Bond angles Chemistry A level. 7 terms. Andrew_Forsyth4. A Level Chemistry Bond Shapes. 14 terms. charlotte_2315. Sets found in the same folder. AQA A-Level Chemistry - Atomic Structure. 38 terms. molly_joy_froggatt. AQA A-Level Chemistry - Bonding. 49 terms.

Shapes of Simple Molecules & Ions (1.5.1) AQA A Level Chemistry Revision Notes 2017 Save My
The bond pairs are at an angle of 120° to each other, and their repulsions can be ignored. Now consider the final structure. Each lone pair is at 90° to 2 bond pairs - the ones above and below the plane. That makes a total of 4 lone pair-bond pair repulsions - compared with 6 of these relatively strong repulsions in the last structure.

Bonding Shapes and Angles Teaching Resources
Common bond angles: 2 Electron Pairs on a single atom form 180° bond angles. 3 Electron Pairs on a single atom form 120° bond angles. 4 Electron Pairs on a single atom form 109.47 (1220… = ) ° bond angles. 6 Electron Pairs on a single atom form 90° bond angles. 2 Lone Pairs and 2 Bonding Pairs on a single atom form a 104.5° bond angle.