Diagnostics Free FullText A New Anatomical Classification for Tibialis Posterior Tendon
Definition Origin: Tibia, fibula Insertion: Navicular, medial cuneiform Artery: Posterior tibial artery Nerve: Tibial nerve Action: Inversion of the foot, plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle Antagonist: Tibialis anterior muscle Description:

Tibialis Posterior Allied Anatomy
The tibialis posterior (TP) muscle has a vital role during gait; via multiple insertion points into the tarsal bones it acts as the primary dynamic stabiliser of the rearfoot and medial longitudinal arch (MLA) [1, 2].The significance of TP function is evident when the muscle and tendon are dysfunctional, whereby stability of the foot is compromised and is associated with a progressive flatfoot.

Tibialis Posterior Origin and Insertion Anatomy and physiology, Anatomy, Med school
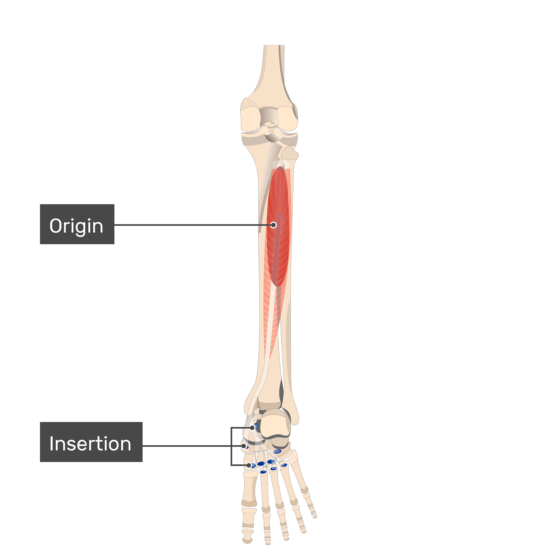
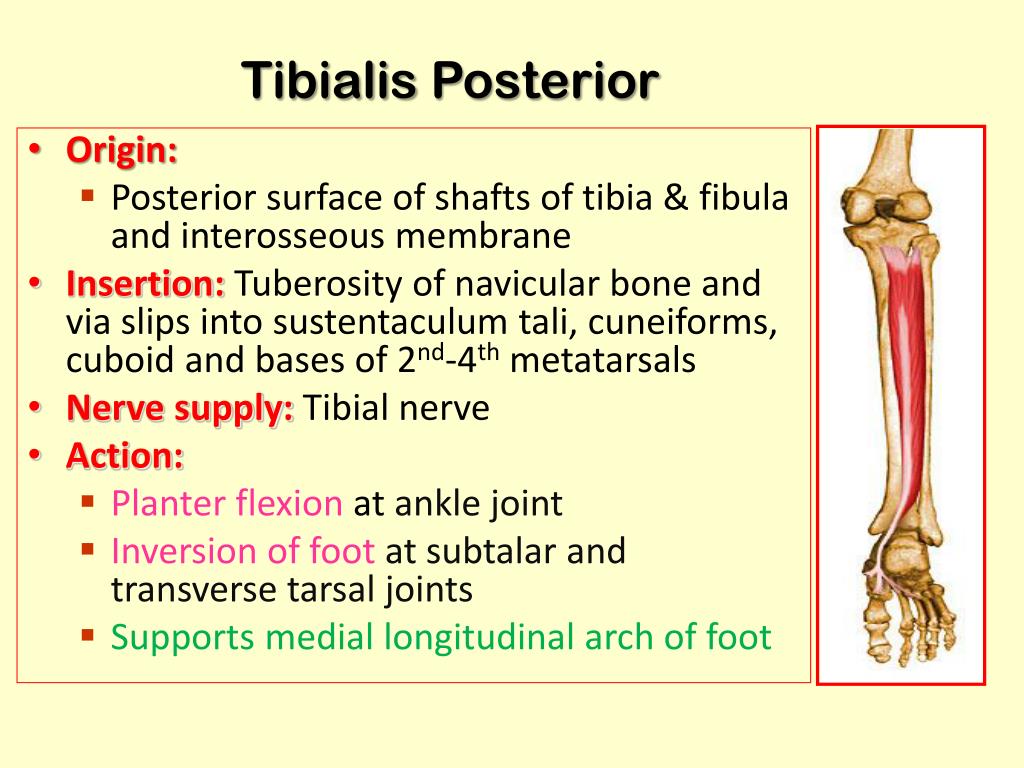
Tibialis Posterior Origin: Posterior aspect of interosseous membrane, superior 2/3 of medial posterior surface of fibula, superior aspect of posterior surface of tibia, and from intermuscular septum between muscles of posterior compartment and deep transverse septum

Tibialis Posterior Muscle Geelong Myotherapy & Wellness Centre
The tibialis posterior is a muscle within the deep compartment of the posterior leg. Is it located between the flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus muscles.

Image result for tibialis posterior origin and insertion Musculoskeletal system, Muscle and
Description The Tibialis Posterior is located deep in the posterior compartment of the lower leg and situated between the Flexor Digitorium Longus and the Flexor Hallucis Longus. It is a key stabilising muscle supporting the medial arch of the foot. Origin The origin of the muscle is [1] : Proximal postero-lateral aspect of the tibia.

Tibialis Posterior Muscle Dr. Justin Dean
⭐ Tibialis Posterior Muscle Anatomy ⭐ 💪 Origin: Posterior surface of tibia, posterior surface of fibula, posterior interosseous membrane. 💪 Insertion: Navicular bone tubercle,.
Tibialis Posterior Muscle Attachments, Actions & Innervation GetBodySmart
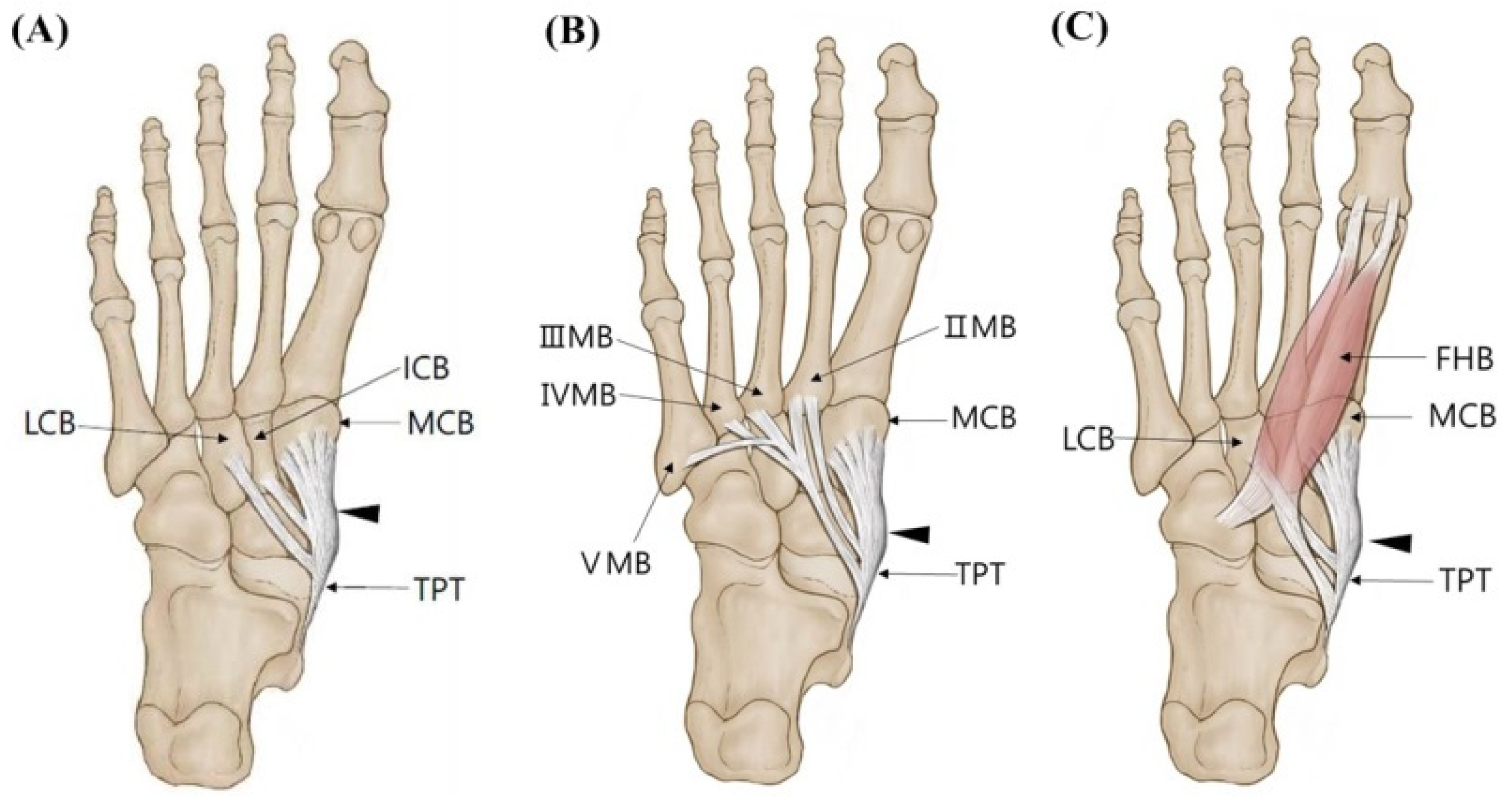
The described anatomical insertion of the TPT may vary according to the geographical origin, ethnicity, and the number of examined specimens. Nevertheless, the sample size of 41dissected feet constitutes a good sample size.. In conclusion, this study adds to current knowledge on the anatomical insertion of the tibialis posterior tendon. The.

Tibialis Posterior Muscle Calf and Foot Pain The Wellness Digest
The tibialis posterior muscle is the most central of all the leg muscles, and is located in the deep posterior compartment of the leg. It is the key stabilizing muscle of the lower leg . Posterior Tibial Tendonitis Posterior Tibial Tendonitis is a condition that predominantly affects runners and active individuals.

insertion/origin of tibialis posterior and flexors Diagram Quizlet
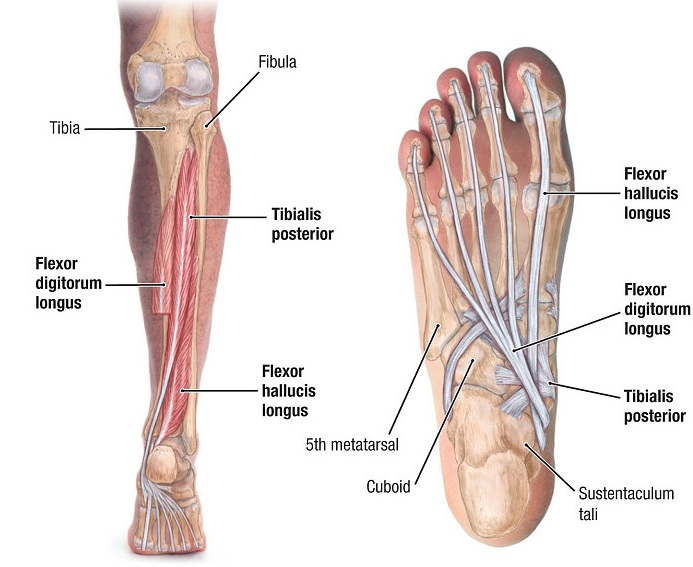
The tibialis posterior muscle, originating from the proximal tibia and fibula, passes distally with a broad insertion on the plantar aspect of the navicular, cuneiform, cuboid, and metatarsal bases and normally functions to invert the subtalar joint and to adduct the forefoot.
M Tibialis Posterior
The tibialis posterior muscle originates from the interosseous membrane, while the posterior surface of the adjoining parts of the tibia, fibula, and muscle belly becomes the tibialis posterior tendon (TPT) in the distal third of the calf.

Musculoskeletal Anatomy Quiz The bones muscles and muscular
The tibialis posterior muscle originates from the: - lateral aspect of the area of the posterior surface of the tibia that is located inferior to the soleal line; - medial aspect of the proximal two thirds of the posterior surface of the fibula; - posterior aspect of the adjacent interosseous membrane of leg; - adjacent intermuscular septa.
Tibialis Posterior Origin, Insertion, Anatomy and Function
Tibialis posterior. The tibialis posterior muscle is a relatively small muscle located within the back side of the calf. It is also the most centrally located muscle in the leg, arising from the.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/tibialis-posterior-muscle/q1O0SzDtl6MmYT8VDBHTw_YVKMLfwiC9N6pxKvYwkTIQ_9vsSyj16ei_M._tibialis_posterior_NN_1__1_.png)
Tibialis posterior Origins, insertions and actions Kenhub
Introduction. The tibialis posterior (TP) muscle has a vital role during gait; via multiple insertion points into the tarsal bones it acts as the primary dynamic stabiliser of the rearfoot and medial longitudinal arch (MLA) [1,2].The significance of TP function is evident when the muscle and tendon are dysfunctional, whereby stability of the foot is compromised and is associated with a.
PPT Posterior Compartment of the Leg PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4700198
Soleal line: oblique line located on the posterior tibia and serves as the origin for the soleus, flexor digitorum longus, and tibialis posterior muscles. Serves as the origin or insertion point of many muscles including tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, soleus, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, sartorius, gracilis, quadriceps femoris, semimembranosus, semitendinosus.
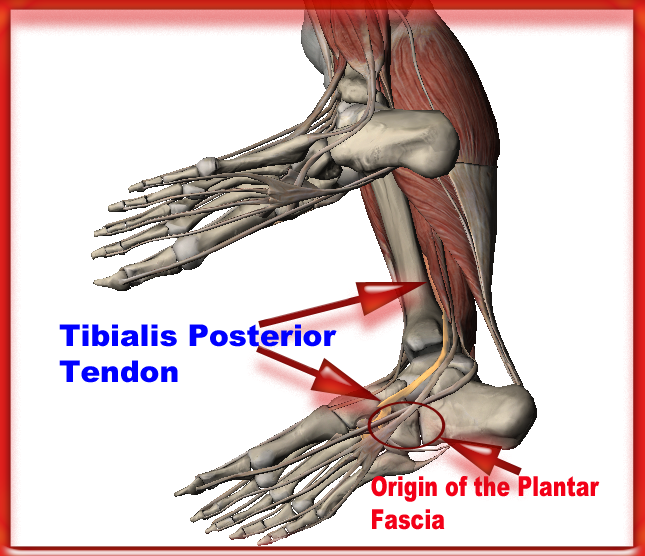
Endurance Athlete Consulting by Senska Physical Therapy Plantar Fasciitis or Tibialis Posterior
The tibialis posterior muscle (TPM) is the deepest muscle of the deep posterior compartment of the lower leg. Its long muscle belly arises from the posterior aspect of the interosseous membrane and superior two-thirds of the posterior and medial surface of the fibula, and the superior aspect of the proximal tibia.

Tibialis Posterior Origin And Insertion
Tibialis posterior is attached between the bones of the leg and the foot. The muscle consists of two parts close to its origin; medial and lateral. The medial portion arises from the upper two-thirds of the posterior surface of tibia, inferior to the soleal line, and from the posterior surface of interosseous membrane of leg.